Keyword [ChestX-ray14]
Li Z, Wang C, Han M, et al. Thoracic disease identification and localization with limited supervision[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2018: 8290-8299.
1. Overview
1.1. Motivation
- Medical training data rarely includes more than global image-level labels as segmentations are time-consuming and expensive to collect
In this paper, it proposes a architecture
- learn at multiple resolutions while generating saliency maps with weak supervision
- parameterize the Log-Sum-Exp pooling function with a learnable lower-bounded adaptation (LSE-LBA)
1.2. Disease
- Enlargement. width of the heart is measured to be 50% or greater than the width of the thoracic cage
- Nodules (肺结节). subtle findings as small as a few millimeters in size and are frequently missed by practitioners even when viewed closely on a high resolution monitor
- Diffuse infiltrative opacification (浸润). in the periphery of the lung is often more easily noted from a global view. But closer inspection of the anomalous region is often required to narrow the differential diagnosis and determine followup
1.3. Contribution
- multi-resolution with MIL
- LSE-LBA

1.4. Related Work
- Wang. ChestX-ray14 (one resolution, non-adaptive pooling)
- Li. upsample or downsample to PxP grids
- Chexnet
- Yao. leverage interdependencies among 14 diseases
- Guan. attention guided CNN
- Kumar. cascaded multiple predictions
- Tienet. additional radiology reports
2. Methods
2.1. Network

ResNet line. f identity connection
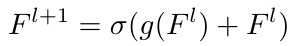
enseNet line

coarse-to-fine. U denote upsample
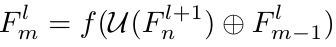
2.2. Pooling Function
Noisy-OR (NOR)
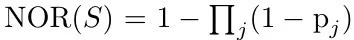
Generalized-mean (GM)

Log-Sum-Exp
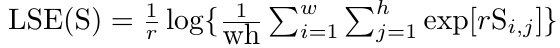
Log-Sum-Exp Pooling with Lower-bound Adaptation (LSE-LBA)

- larger r_0 encourages the learned saliency map to have less diffuse modes.
3. Experiments
3.1. dataset
- 1024x1024 to 512x512, [0, 1]
- data augmentation
- resize [0.25, 0.75]
- translate in for direction [-50, 50]
- rotate [-25, 25]
- not use other clinical information, such as age and gender
- official split

3.2. Comparison

- when r_0 is large, the performance of disffused abnormalities degrades, such as atelectasis(扩张不全), cardiomegaly (心脏扩大), effusion (积液) and pneumonia (肺炎)

- increasing r_0 results in overall sharper saliency maps